Soil erosion and its side effects in changing climatic conditions
The State of Gujarat accounts for 6.2% of the total geographical area of India and 5% of the total population.

Gujarat is one of the fastest-growing states in India. The last decade has seen tremendous progress in the fields of industry, energy, and agriculture. The State of Gujarat accounts for 6.2% of the total geographical area of India and 5% of the total population. The State of Gujarat contributes about 7.2% to the growth rate of India and similarly contributes about 16% to the production of industrial products. Thus the growing population burden in the country and the state forces the production of agricultural and industrial products to increase. Thus, the bounty given by nature is the haphazard use of products like land, water, and forest.
In the wake of urbanization and industrialization, the natural bounty is greatly wasted or its productivity is declining. Land loses its productivity due to poor cropping systems, mismanagement of land, and on the other hand due to increasing population, urbanization, deforestation pose environmental hazards. Incidents such as non-seasonal rains, heavy rains, and droughts in the form of fruits cause soil erosion and hence severely damage the productivity of arable and non-arable land. Thus, soil erosion plays a very important role in reducing soil productivity.
What is soil erosion?
Soil erosion is the process of separation, migration, and stabilization of soil particles by water or wind.
Causes of soil erosion :
The surface of the soil undergoes a lot of climatic changes like high and low temperature, humidity, rain, wind, heat. As a result, the process of soil formation in the surface of the surface continues and in the same way, due to rain and wind, the soil particles migrate and stabilize. But human-induced activities such as deforestation, urbanization, close cropping systems, unsuitable farming practices, seasonal rainfall due to environmental imbalances, cyclones, excess rainfall, and droughts increase the rate of land erosion.
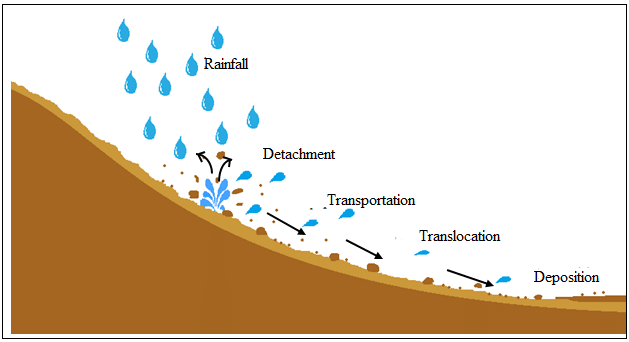
Thus, the rate of soil formation and the rate of soil erosion are similar in the natural cycle. But the reasons for the increase in human-induced activities mentioned above are the rate of soil erosion more than the rate of soil formation and consequently the fertility of the soil surface increases as the erosion of the fertile soil increases.
The role of wind and water in arid and semi-arid areas is important in the process of migration and stabilization of the 3 layers of land separated from each other. Thus, wind or water acts as a carrier. Factors affecting soil erosion include deforestation of trees and grasses, overgrazing, improper farming practices, and improper maintenance of discharge areas. However, some natural factors follow.
Factors affecting soil erosion :
The role of wind and water in arid and semi-arid areas is important in the process of relocation and stabilization of the 3 layers of land. Thus, wind or water acts as a carrier. Factors affecting soil erosion include deforestation of trees and grasses, overgrazing, improper farming practices, and improper maintenance of discharge areas. However, some natural factors follow.
Climatic Factors:
Due to the amount, intensity, and frequency of rainfall falling on the surface of the soil, the rate of groundwater filling is affected.
Temperature:
Due to high-low temperatures, the physical condition of the soil fluctuates and plays an important role in the formation of new soil.
Geographical Factors:
The slope of the ground surface, the length of the slope, the intensity of the slope, the elevation of the surface, and the roughness are the factors most affecting the flowing water. On steep slopes, the flowing water gets very fast so a lot of soil flows.
Land:
Physical properties of soil such as particle size, bonding between two particles, soil texture, and physical composition of soil are factors that contribute to soil erosion. In sandy soils, 3 particles are easily separated and flow, whereas 3 particles of black-clayey soil are not easily separated and flow in small amounts.
Tree/grass cover:
The green cover of trees or grass on the surface of the soil dissipates the energy contained in the raindrops thus reducing the amount of soil erosion.
Biological Factors:
Behavior-induced or animal-induced activities such as overgrazing, improper farming practices, human-animal settlement, stimulation of erosion-increasing activities, and loss of erosion prevention or reduction factors play a significant role in soil erosion.
Therefore, land erosion can be reduced only if the maximum amount of rainwater collected on the land descends into the soil and the remaining amount of flow is also leveled with technology like check dam. Thus, soil erosion can be controlled only by the trees, forests, and green coverings on the surface of the earth.
According to a report, about 550 million tons of soil is eroded annually in all of India due to erosion of one millimeter thick surface of the land surface, and per unit area, the rate of erosion in India is 16.4 tons per hectare per year i.e. one hectare of land. Every year, 16.4 tons of fertile soil is eroded.






