Different methods of fertilizing in Fruits
Such vertical farms have been developed by a company called Green Sense Farm in China, Hong Kong and Macau.

Such vertical farms have been developed by a company called Green Sense Farm in China, Hong Kong and Macau. The main reason for the slowdown in the introduction of vertical framing was the high cost of LED lamps. Now that the price of this type of lame has come down, this type of farming has gained momentum. This type of farming should be encouraged because it is very important for food security in the coming days and this type of farming is very necessary in the age of global warming as it has carbon footprints.
There are mainly three types of fertilizers
(1) Organic fertilizer (2) biological fertilizer (3) chemical fertilizer
Organic fertilizer
These are natural fertilizers that are prepared from vegetable as well as animal residues from which gradually available elements are obtained. As well as the physical condition of the soil is maintained and added to the structure. E.g. Manure, compost, earthworm manure (vermi compost), flour.
Biological fertilizer
These is a ecofriendly fertilizer. Due to the use of Biological fertilizer it maintain the biological balance of the soil. And increases the biochemical process required for the availability of nutrients. E.g. Rhizobium, Azetobacter, Phosphate culture.
Chemical fertilizer
These are synthetic fertilizers, from which the prescribed elements get to the plants quickly. E.g. Urea, DAP, Superphosphate, Murate of Potash.
Fertilizers are given by different methods mainly for 3 purposes:
(1) To make nutrients easily available to crops
(2) Reduce fertilizer waste
(3) For easy sprinkling
How the nutrition of fruits is different from other crops.
(1) Its roots are more diffuse as well as deeper.
(2) As it is perennial, fruit crops need to add nutrients to the soil every year.
(3) Since fruits have to be harvested every year, more nutrients are taken from the soil and therefore nutrients are removed from the soil.
(4) Due to the height of the fruit tree, the stagnant nutrients do not reach the top of the tree.
(1) Methods of application of organic manure in fruits:
Most of the organic fertilizers are applied at the base 15-20 days before sowing or planting of the crop.
(2) Methods of application of Biological manure in fruits:
Liquid organic fertilizers can be applied by drip irrigation in the fruit, grooming the seedlings, as well as spraying on the leaves.
Fertilizers to be given in solid form
(1) Powder (single superphosphate)
(2) Crystals (ammonium sulphate
(3) Prills (urea, diammonium phosphate, superphosphate)
(4) Granules (Holland granules)
(5) Supernuranes Briquettes)
Method of application of powder or solid form fertilizers:
Fertilizing
In this method, before the primary tillage, the manure is applied by hand on all the soil, then it is plowed and mixed in the soil. Manure, flour, compost manure and fertilizers applied in bulk are given by this method.
Disadvantages associated with this method
- Nutrients cannot be fully utilized by plant roots.
- Weed growth is high.
- Nutrients settle in the soil as it comes in contact with large amounts of soil.
Ring around the fruit tree and give fertilizer (ring placement)
A circular ring is made around the fruit tree and compost is mixed in the soil with a shovel. As long as there is a girth of the tree, fertilizing the area provides nutrients from all the roots. Normally fertilizer is given at 3 to 4 weeks after planting. This method provides adequate nutrients to each plant and reduces weeds as well as increases productivity.
Benefits of Fertilizer Placement
- When manure is applied, there is minimal contact between the soil and the manure, and therefore the regulation of nutrients is greatly reduced.
- Fertilizer is not wasted.
- The response to fertilizer residues is usually higher.
- The use of fertilizers by plants is increased.
- Nitrogen loss is reduced by leaching.
- More phosphorus can be used when stabilizing.
Liquid Fertilizer
- Liquid form fertilizers are given from irrigation water or directly.
- Farmers use more liquid fertilizers due to ease of handling, less labor required and mixing with herbicides.
Methods of applying liquid fertilizer
(1) Starter Solution
In this method a low concentration solution (liquid) of manure is prepared in which the seeds as well as the roots of the plants are boiled and sprinkled on the poles so that the plants grow faster and grow faster and better.
(2) Fertilization with Drip irrigation
Fertilization is a very effective and efficient method of fertilizing by irrigation method. The nutrients required for plant growth and development are found. By this method every orchard gets fertilizer in proper quantity and available form with water which is key for more production and quality.
Fertilizers in powder and solid form are used in fertilization depending on their solubility. Important nitrogenous fertilizers like ammonium phosphate, urea, anhydrous ammonia, ammonium nitrate and calcium nitrate can be used. Potassium can be given by potassium sulphate, potassium chloride and potassium nitrate which are completely water soluble fertilizers. Liquid fertilizers contain more than one nutrient. It is more convenient to give liquid fertilizers in fertigation as they are completely soluble. Liquid fertilizers are generally pure and do not produce salts. Chemicals other than fertilizers such as herbicides, herbicides can also be given.

(3) Foliar application on leaf:
In this method, if the nutrient deficiency is more, it is given on permanent fruit in its form for quick recovery. It does not waste nutrients in the soil. A low concentration solution (less than 1 to 2%) is prepared for spraying a nutrient or a mixture of nutrients. In general, nitrogen and micronutrients are treated as foliar. In this method along with manure, pesticide as well as fungicide can also be sprayed.
Disadvantages associated with this method
(1) The leaves of the plant get burnt if a high concentration of liquid is used.
(2)Due to the low concentration, only a small amount of nutrients can be given in a single ounce.
(3)For moderate to high fertilizer doses and more often applications have to be given.
(4)This is a more expensive method than applying to the ground.
(4) Fertilized by ejection into the soil
Liquid fertilizers such as anhydrous ammonia are injected directly into the soil. Liquid organic fertilizers can also be applied with this method.
(5) Aerial application
In areas where manure cannot be applied directly to the soil, manure is given by air, especially in mountainous areas, forest lands, grasslands or large sugarcane fields.
Care before and after fertilizing
(1) Weeds should be removed before fertilizing as weeds compete with plants for nutrients, moisture and light.
(2) Weeds should be removed before fertilizing as weeds compete with plants for nutrients, moisture and light.
(3) Adequate moisture in the soil is essential when applying fertilizer.
(4) The drip system should be operated at the prescribed pressure during fertilization otherwise the distribution of manure will be uneven.
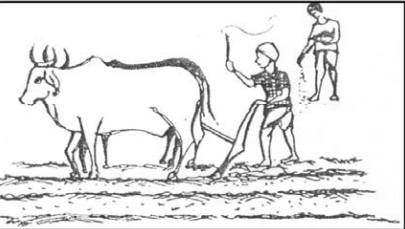
Fertilizing
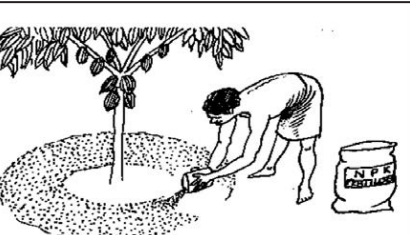
Give Fertilizer to fruit plant

Band placement

Fertigation
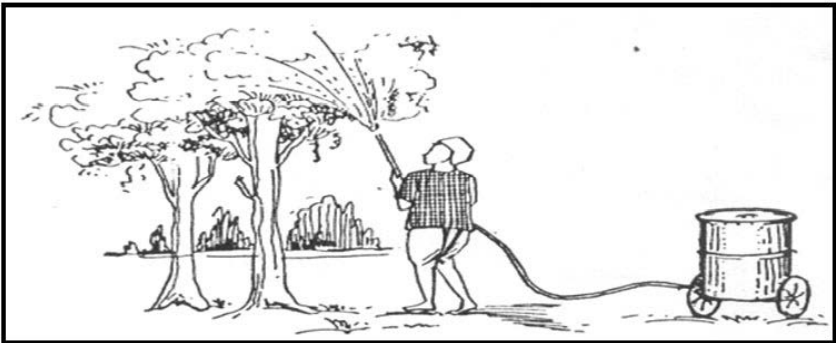
Aerial application






